Senior Developer Landscape In 2026 - Part I
What it takes to be a frontend developer In 2026.
Feb 4, 2026 • Subash Maharjan

On This Page
The Senior Frontend Landscape (2026)
In 2026, the senior frontend role has shifted from simply building components to orchestrating intelligent, performance-first systems. Employers now look for experts who can solve complex domain-specific problems rather than generalists.
Challenge: Which specific tech stack (e.g., React/Next.js vs. Vue/Nuxt) have you spent the most time with recently?
Essential Technical Mastery
1. Deep React
In 2026, being "Senior" in React means moving beyond simple UI component design to managing the infrastructure of the rendering lifecycle. You are orchestrating how data flows from the server to the user's screen with surgical precision.
React is now considered "infrastructure." Beyond basic hooks, you must master:
- React Server Components (RSC)
- Streaming rendering
- Hydration boundaries
React Server Components (RSC)
RSC is the most significant shift since Hooks, turning React into a dual-component model.
- The Zero-Bundle Rule: Identify "Server-only" components to ship zero JavaScript for static UI parts.
- Server Actions as Infrastructure: Replace manual
fetchboilerplate with Server Actions to create a seamless bridge between client and server. - Direct Database Access: Comfort with fetching data directly in components using Prisma or Drizzle ORM instead of separate API layers.
Orchestrating Streaming & Suspense
Modern performance is about perceived speed through streaming.
- Progressive Rendering: Use
<Suspense>boundaries to stream HTML chunks. The user sees the "shell" immediately while heavy data loads. - The "Streaming Lifecycle": Design UIs that handle transitions gracefully—from "thinking" to "finalizing"—eliminating UI flickers or layout jumps.
Selective & Adaptive Hydration
The "All-or-Nothing" hydration of the past is gone.
- Interaction Prioritization: Understand how React 18+ prioritizes hydrating the specific element a user clicks first.
- Reducing TBT (Total Blocking Time): Defer hydration of non-critical elements (like footers) to reduce main-thread blockage by up to 40%.
React Compiler
With the compiler now standard, your role shifts from manual memoization to architectural trade-offs.
- Pure Functions: Strict adherence is required. You must debug optimization failures caused by unstable "shapes" or side effects.
- Stable State Ownership: Strategic placement of state to minimize re-renders that even a compiler cannot resolve.
Challenge: Are you currently using a meta-framework like Next.js or Remix, or are you working with a custom-built React architecture?
2. Performance Engineering
In the current market, Performance Engineering has moved from a post-launch audit to a design-time requirement. As a senior developer, you are expected to prevent bottlenecks before they are even measured by a profiler.
Performance is no longer an "extra." You must deeply understand:
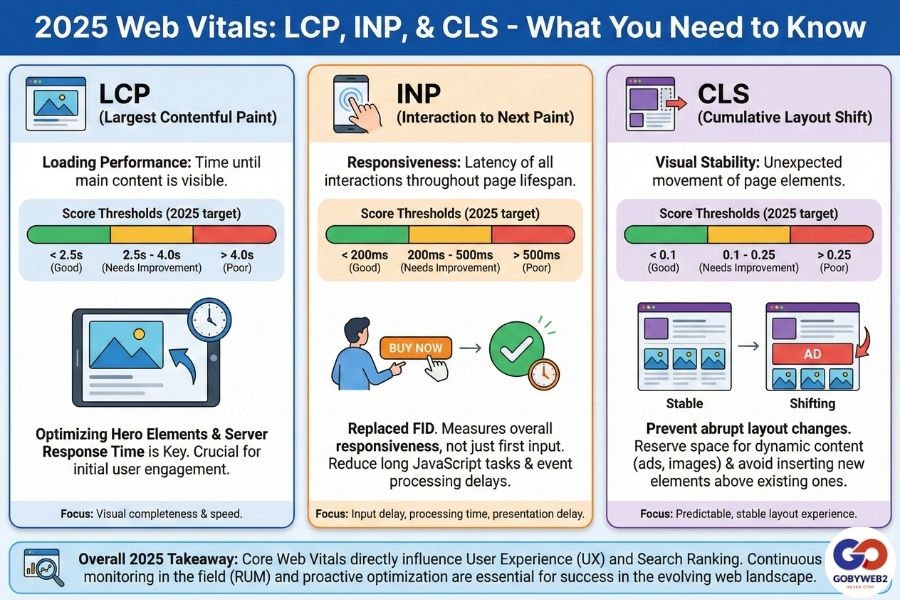
- Core Web Vitals (LCP - Largest Contentful Paint, INP - Interaction to Next Paint, CLS - Cumulative Layout Shift)
- Memory management in long-running SPAs
- Minimizing "layout shifts" (CLS)
Mastering Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
INP has officially replaced First Input Delay (FID) as the primary interactivity metric, measuring responsiveness throughout the entire page lifecycle.
- The 200ms Bar: Interactions must stay under 200ms to be categorized as "Good."
- Yielding and Chunking: Use the
scheduler.yield()API for heavy logic to return control to the main thread, allowing the browser to paint a frame before resuming. - Avoid Layout Thrashing: Prevent synchronous layout calculations during interactions.
Managing the Modern "Hydration Bottleneck"
By 2026, the primary performance challenge is the "hydration cost" of shipping excessive JavaScript.
- Selective Hydration: Use
<Suspense>and dynamic imports to prioritize interactive elements. - Zero-Bundle Architecture: Move static UI to Server Components to ship zero client-side JavaScript for those segments.
Data-Intensive UI Strategies
| Strategy | Implementation |
|---|---|
| Virtualization | Keep DOM size below 1,400–2,500 elements for long lists. |
| Offloading | Move sorting, filtering, or heavy aggregation to Web Workers. |
| Pagination | Use IntersectionObserver for seamless, performant data fetching. |
Advanced Profiling & Tooling
Diagnosis is as important as the fix. You must prove why a site is slow.
- CPU Throttling: Always profile with 4x or 6x slowdown to simulate real-world mobile experiences.
- Real User Monitoring (RUM): Prioritize Field Data over Lab Data to identify failing interactions in production.
Challenge: Do you typically use built-in browser APIs (like requestIdleCallback) or framework-specific tools (like React's startTransition) for managing task priorities?
3. Advanced JavaScript Fundamentals
In 2026, a senior developer’s value lies in their ability to debug the "un-debuggable." Mastery focuses on predictability, memory efficiency, and deep engine specifications.
Frameworks change, but you must be an expert in the event loop, async behavior, and closures to solve the "stale state" bugs common in modern apps.
Advanced Concurrency & The Event Loop
Move beyond "async is non-blocking" to master task prioritization.
- Microtask Starvation: Prevent infinite microtask loops from freezing the UI by understanding the Event Loop processing.
- The Rendering Loop: Sync visual updates with
requestAnimationFrameto ensure they execute right before the browser repaints.
Memory Management & Garbage Collection
Performance is often a memory issue in disguise.
- Weak References: Utilize
WeakMapandWeakSetfor metadata to allow objects to be garbage collected. - Closure Retention: Identify when a closure accidentally retains large objects in its lexical scope.
Strategic Use of Modern ES Features (ES2025+)
- Temporal API: The new standard for handling complex time zones without external libraries.
- Records and Tuples: Deeply nested immutable data structures for fast referential equality checks.
- Pattern Matching: Replace complex
if/elsechains with declarative logic.
Challenge: Are you comfortable using Chrome DevTools' Memory tab to take heap snapshots and identify detached DOM nodes?
4. TypeScript by Default
In 2026, TypeScript is the documentation, the validation layer, and the contract between server and client. Seniority means writing code where types are inferred, not forced, creating a self-healing codebase.
Type-Safe Data Orchestration
TypeScript now bridges the "Network Chasm" created by React Server Components (RSC).
- End-to-End Safety: Use tools like tRPC or Drizzle ORM to share types directly from the database schema to the UI.
- Abolishing
any: In senior-led repos,anyis a build-blocking error. Mastery of Generics and Conditional Types is required.
Advanced Patterns for Seniority
Handling complex logic requires moving beyond basic interfaces:
- Discriminated Unions: Prevent "impossible states" (e.g., having both
dataanderrorsimultaneously) by modeling state predictably. - Mapped Types & Template Literals: Create high-level utility types that transform data structures for robust design systems.
- Zod Integration: Bridge the gap between static types and runtime reality. Use Zod to validate API responses.
Challenge: Have you moved your projects to
strict: trueyet, or are you still working through legacyanytypes?
You Might Also Like
Senior Developer Landscape In 2026 - Part I
What it takes to be a frontend developer In 2026.
Artificial Intelligence for Frontend
A guide to understanding AI and its impact on frontend technology.
The Chautari Newsletter
Subscribe for deep dives into frontend architecture, AI integration, and engineering insights from the heart of the Himalayas.
